HTTP error 403 — Forbidden
Generally, the HTTP error 403 — Forbidden means that access to the file/folder you are trying to open has been denied, either on purpose or due to a misconfiguration . It’s probably because the site owner has limited access to it and you don’t have permission to view it. FORBIDDEN: Status code (403) indicating the server understood the request but refused to fulfil it.
For end-users
The vast majority of the time, there’s not much you can do to fix things on your end. Still, there are some things you can try.
- Refresh the Page
- Double Check the Address
- Clear Browser Cookies and Cache
- Check firewall settings
- Deactivate browser extensions
- Try Again Later
- Contact website administrators
For site administrators
There are three common causes for this error
- An empty website directory
- No index page
- Permission and Ownership error
An empty website directory
Make sure that your website content has been uploaded to the correct directory on your server.
Plesk server
When someone creates a website, Plesk not only adds a new virtual host to the web server but also creates the site’s directory structure e and fills the directories with certain initial content. These directories are located in the corresponding virtual host directories :
By default it creates the directories below:
— domain’s root directory (may be changed in the Domains > example.com > Hosting Settings);
When you connect with your FTP user, you just need to navigate into the httpdocs directory. Moreover, be sure to replace example.com with your actual domain name.
cPanel server:
The /home/example/public_html/ folder is the web root for your primary domain name. This means that public_html is the folder where you put all website files which you want to appear when someone types your main domain. when someone types your domain name into their browser, whatever is in your public_html directory is what will be shown to them.
When you connect with your FTP user, you just need to navigate into the public_html directory. Be sure to replace example with the name of your cPanel account username.
Microsoft turn off the most basic features by default. Go to Turn Windows features on or off.

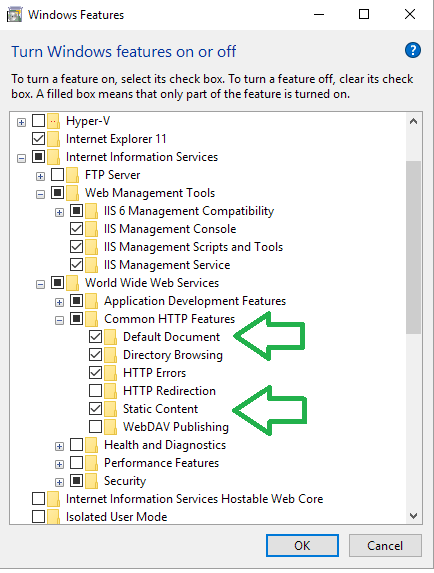
No index page
The default document is the first file the server sends when someone visits your site. The default document is usually index.html or index.php, but you can configure it to be any file you want.
Index files option is set to Default at:
To resolve this 403 Forbidden error, upload an index page to your httpdocs or public_html directory.
If you already have a home page called something else — example.html , you have a couple of options to change it:
- Rename your home page to index.html or index.php.
- Set up a redirect on the index page to your real home page.
- Set a different default home page in your .htaccess file.
HTTP Error 403.14 — Forbidden in IIS
The Web server is configured to not list the contents of this directory.
In IIS, a default document is not configured for the requested URL, and directory browsing is not enabled on the server.
How to enable directory browsing?
- Go to the IIS Express install directory.
Run appcmd set config /section:system.webServer/directoryBrowse /enabled:true to enable directory browsing at the server level.
Moreover, verify that the configuration/system.webServer/directoryBrowse@enabled attribute is set to true in the site or application configuration file
Permissions and ownership errors
HTTP Error 403.14 – Forbidden error can also be caused by incorrect ownership or permissions on your website content files and folders.
Permissions
Additionally, if you know PHP runs as the user and not as «apache», then you can set PHP files to 600, for an extra level of security, eg:
Ownership
The concept of owner and groups for files is fundamental to Linux. Every file is associated with an owner and a group. You can use chown and chgrp commands to change the owner or the group of a particular file or directory.
Every Linux system have three types of owner:
- User: A user is the one who created the file. By default, whosoever, creates the file becomes the owner of the file. A user can create, delete, or modify the file.
Group: A group can contain multiple users. All the users belonging to a group have same access permission for a file.
Users and groups can be locally managed in /etc/psswd or /etc/group .
Plesk server: domain — example.com, domainuser — FTP user
cPanel server: account user — example
The chown command is used to change file ownership settings. The basic syntax is:
Nginx 403 forbidden error
Nginx 403 Forbidden error is a status code generated and displayed to the user when a client tries to access a part of the webserver with insufficient permissions. When nginx access a directory, it tries to index it and return the list of files inside it to the browser/client, however by default directory indexing is disabled, and so it returns the error » Nginx 403 error: directory index of [folder] is forbidden».
Incorrect Index File
The try_files tries the literal path you specify in relation to the defined root directive and sets the internal file pointer. If you have directory indexing off, and is having this problem, it’s probably because the try_files you are using has a directory option:
Incorrectly set permissions
This error can also result from files and directories having incorrectly set permissions. In order to resolve this , change the directories permission to 755 and the file permissions to 644 . Make sure that the user running the Nginx process owns the files. For example, set user to www-data:
Finally, set the directory and file permissions as:
«Access Denied» or other errors when you access or work with files and folders in Windows
Summary
When you try to access or work with files and folders in Windows, you experience one or more of the following issues:
Issue 1: You receive an «Access Denied» error message or a similar message.
Issue 2: You cannot access, change, save, or delete files and folders.
Issue 3: You cannot open a file or folder after you install a new version of Windows.
Resolution
To resolve a particular issue, follow the steps for the issue that best describes your situation. Use the method for your version of Windows.
Note You may not always receive an “Access Denied” error message for these kinds of issues. If particular steps do not resolve the issue, try a different set of steps.
Cause An «Access Denied» error message can occur for one or more of the following reasons:
The folder ownership has changed.
You do not have the appropriate permissions.
The file is encrypted.
You may not have ownership of a file or folder If you recently upgraded your computer to Windows 8 from an earlier version of Windows, some of your account information may have changed. Therefore, you may no longer have ownership of some files or folders. You might be able to resolve this issue by restoring your ownership of the files and folders.
To take ownership of a file or folder, follow these steps:
Press and hold the folder that you want to take ownership of, then tap Properties. (If you are using a mouse, right-click the folder, and then click Properties.)
Tap or click the Security tab, tap or click Advanced, then tap or click Change. If you are prompted for an administrator password or for confirmation, type the password or provide confirmation.
Type the name of the person that you want to give ownership to, and then click Check Names.
Note The account name for the person that you are assigning ownership to is displayed.
If you want this person to be the owner of the files and subfolders that are contained in this folder, select the Replace owner on subcontainers and objects check box.
You may not have the appropriate permissions Issues that you experience when you try to access files and folders may be related to permissions. Permissions are rules that determine whether you can access or change files and folders. To check permissions on a file or folder, follow these steps:
Press and hold or right-click the file or folder, and then click Properties.
Tap or click the Security tab.
Under Group or user names, tap or click your name to see the permissions that you have.
To open a file, you have to have the Read permission. To change the permissions of a file or folder, follow these steps.
Important You must be logged on as an administrator to change permissions on files and folders.
Press and hold or right-click the file or folder, and then tap or click Properties.
Tap or click the Security tab.
Under Group or user names, tap or click your name to see the permissions that you have.
Tap or click Edit, tap or click your name, select the check boxes for the permissions that you must have, and then click OK.
The file or folder may be encrypted Encryption can help protect files and folders from unwanted access. You cannot open an encrypted file or folder without the certificate that was used to encrypt it. To determine whether a file or folder is encrypted, follow these steps:
Press and hold or right-click the file or folder, and then tap or click Properties.
Tap or click the General tab, and then tap or click Advanced.
If the Encrypt contents to secure data check box is selected, you have to have the certificate that was used to encrypt the file or folder to be able to open it. In this situation, you should obtain the certificate from the person who created or encrypted the file or folder, or have that person decrypt the file or folder.
You may not have ownership of a file or folder If you recently upgraded your computer to Windows 7 from an earlier version of Windows, some of your account information may have changed. Therefore, you may no longer have ownership of some files or folders. You might be able to resolve this issue by restoring your ownership of the files and folders.
To take ownership of a file or a folder, follow these steps:
Right-click the folder that you want to take ownership of, then click Properties.
Click the Security tab, click Advanced, then click the Owner tab.
Note If you are prompted for an administrator password or for confirmation, type the password or provide confirmation.
Click the name of the person that you want to give ownership to.
If you want this person to be the owner of files and subfolders in this folder, select the Replace owner on subcontainers and objects check box.
You may not have the appropriate permissions Issues that you experience when you try to access files and folders may be related to permissions. Permissions are rules that determine whether you can access or change files and folders. To determine the permissions of the file or folder, follow these steps:
Right-click the file or folder, then click Properties.
Click the Security tab.
Under Group or user names, click your name to see the permissions that you have.
To open a file, you have to have the Read permission. To change permissions on a file or folder, follow these steps.
Important You must be logged on as an administrator to change permissions on files and folders.
Right-click the file or folder, and then click Properties.
Click the Security tab.
Under Group or user names, click your name to see the permissions that you have.
Click Edit, click your name, select the check boxes for the permissions that you must have, and then click OK.
For more information about permissions, see What are permissions?.
The file or folder may be encrypted Encryption can help protect files and folders from unwanted access. You cannot open an encrypted file or folder without the certificate that was used to encrypt it. To determine whether a file or folder is encrypted, follow these steps:
Right-click the file or folder, and then click Properties.
Click the General tab, then click Advanced.
If the Encrypt contents to secure data check box is selected, you have to have the certificate that was used to encrypt the file or folder to be able to open it.
You should obtain the certificate from the person who created or encrypted the file or folder, or have that person decrypt the file or folder.
Cause A problem that prevents you from accessing or working with files and folders can occur for one or more of the following reasons:
The folder ownership has changed
You do not have the appropriate permissions
The file is encrypted
The file is corrupted
The user profile is corrupted
You may not have ownership of a file or folder If you recently upgraded your computer to Windows 8 from an earlier version of Windows, some of your account information may have changed. Therefore, you may no longer have ownership of some files or folders. You might be able to resolve this issue by restoring your ownership of the files and folders.
To take ownership of a file or folder, follow these steps:
Press and hold the folder that you want to take ownership of, then tap Properties. (If you are using a mouse, right-click the folder, and then click Properties.)
Tap or click the Security tab, tap or click Advanced, then tap or click Change. If you are prompted for an administrator password or for confirmation, type the password or provide confirmation.
Type the name of the person that you want to give ownership to, and then click Check Names.
Note The account name for the person that you are assigning ownership to is displayed.
If you want this person to be the owner of the files and subfolders that are contained in this folder, select the Replace owner on subcontainers and objects check box.
You may not have the appropriate permissions Issues that you experience when you try to access files and folders may be related to permissions. Permissions are rules that determine whether you can access or change files and folders. To check permissions on a file or a folder, follow these steps:
Press and hold or right-click the file or folder, and then click Properties.
Tap or click the Security tab.
Under Group or user names, tap or click your name to see the permissions that you have.
To open a file, you have to have the Read permission. To change the permissions of a file or folder, follow these steps.
Important You must be logged on as an administrator to change permissions on files and folders.
Press and hold or right-click the file or folder, and then tap or click Properties.
Tap or click the Security tab.
Under Group or user names, tap or click your name to see the permissions that you have.
Tap or click Edit, tap or click your name, select the check boxes for the permissions that you must have, and then click OK.
For more information about permissions, see What are permissions?.
The file or folder may be encrypted Encryption can help protect files and folders from unwanted access. You cannot open an encrypted file or folder without the certificate that was used to encrypt it. To determine whether a file or folder is encrypted, follow these steps:
Press and hold or right-click the file or folder, and then tap or click Properties.
Tap or click the General tab, and then tap or click Advanced.
If the Encrypt contents to secure data check box is selected, you have to have the certificate that was used to encrypt the file or folder to be able to open it. In this situation, you should obtain the certificate from the person who created or encrypted the file or folder, or have that person decrypt the file or folder.
The file or folder may be corrupted Files can become corrupted for several reasons. The most common reason is that you have a file open when your computer crashes or loses power. Most corrupted files cannot be repaired. In this situation, you should either delete the file or restore the file from a backup copy.
For more information about corrupted files and how to fix them, see Corrupted files: frequently asked questions.
Your local user profile may be corrupted Occasionally, Windows might not read your local user profile correctly. This may prevent you from accessing files and folders. In this situation, you may have to use a new local user profile. To create the profile, you must first create a local user account. When the new account is created, the profile is also created. To create a local user account, follow these steps:
Swipe from the right edge of the screen, tap Settings, and then tap Change PC settings. (If you are using a mouse, point to the upper-right corner of the screen, move the mouse pointer down, click Settings, and then click Change PC settings)
In the navigation pane, tap or click Users.
Tap or Click Add a User, then tap or click Can they sign in without a Microsoft account?
Tap or click Local account.
Enter your new account name.
If you want to use a password, enter and verify the password that you want to use. If you decide not to use a password, tap or click Next without entering a password.
Tap or click Finish.
You may not have ownership of a file or folder If you recently upgraded your computer to Windows 7 from an earlier version of Windows, some of your account information may have changed. Therefore, you may no longer have ownership of some files or folders. You might be able to resolve this issue by restoring your ownership of the files and folders.
To take ownership of a file or a folder, follow these steps:
Right-click the folder that you want to take ownership of, and then click Properties.
Click the Security tab, click Advanced, and then click the Owner tab.
Click Edit. If you are prompted for an administrator password or for confirmation, type the password or provide confirmation.
Click the name of the person that you want to give ownership to.
If you want that person to be the owner of files and subfolders in this folder, select the Replace owner on subcontainers and objects check box.
You may not have the appropriate permissions Issues that you experience when you try to access files and folders may be related to permissions. Permissions are rules that determine whether you can access or change files and folders. To check permissions on a file or a folder, follow these steps:
Press and hold or right-click the file or folder, and then click Properties.
Tap or click the Security tab.
Under Group or user names, tap or click your name to see the permissions that you have.
To open a file, you have to have the Read permission. To change permissions on a file or folder, follow these steps.
Important You must be logged on as an administrator to change permissions on files and folders.
Right-click the file or folder, and then click Properties.
Click the Security tab.
Under Group or user names, click your name to see the permissions you have.
Click Edit, click your name, select the check boxes for the permissions that you must have, and then click OK.
For more information about permissions, see What are permissions?.
The file or folder may be encrypted Encryption can help protect files and folders from unwanted access. You cannot open an encrypted file or folder without the certificate that was used to encrypt it. To determine whether a file or folder is encrypted, follow these steps:
Right-click the file, then click Properties.
Click the General tab, and then click Advanced.
If the Encrypt contents to secure data check box is selected, you have to have the certificate that was used to encrypt the file or folder to be able to open it.
You should obtain the certificate from the person who created the file. For more information, see Import or export certificates and private keys.
The file or folder may be corrupted Files can become corrupted for several reasons. The most common reason is that you have a file open when your computer crashes or loses power. Most corrupted files cannot be repaired. In this situation, you should either delete the file or restore the file from a backup copy.
For more information about corrupted files and how to fix them, see Corrupted files: frequently asked questions.
Your user profile may be corrupted Occasionally, Windows might not read your local user profile correctly. This may prevent you from accessing files and folders. In this situation, you may have to use a new local user profile. To create the profile, you must first create a local user account. When the new account is created, the profile is also created.
For more information about how to create user profiles, see Fix a corrupted user profile. After the new user profile is created, you can copy your existing user files to the new profile so that you can access them.
Cause Problems that prevent you from accessing files and folders after you upgrade to a new version of Windows can occur for one or more of the following reasons:
The folder ownership has changed.
The files are being stored in a Windows.old folder from your previous system.
You may not have ownership of a file or folder If you recently upgraded your computer to Windows 8 from an earlier version of Windows, some of your account information may have changed. Therefore, you may no longer have ownership of some files and folders. You might be able to resolve this issue by restoring your ownership of the files and folders.
To take ownership of a file or a folder, follow these steps:
Press and hold the folder that you want to take ownership of, then tap Properties. (If you are using a mouse, right-click the folder, and then click Properties.)
Tap or click the Security tab, tap or click Advanced, then tap or click Change. If you are prompted for an administrator password or for confirmation, type the password or provide confirmation.
Type the name of the person that you want to give ownership to, and then click Check Names.
Note The account name for the person that you are assigning ownership to is displayed.
If you want this person to be the owner of the files and subfolders that are contained in this folder, select the Replace owner on subcontainers and objects check box.
You have to recover files from the Windows.old folder If you recently upgraded your computer to Windows 8 from an earlier version of Windows, and you did not reformat the hard disk, you might still be able to access your old files from the Windows.old folder.
To fix this problem automatically, click the Fix it button or link. In the File Download dialog box, click Run, and then follow the steps in the Fix it Wizard. If you prefer to fix this problem yourself, go to the «Let me fix it myself» section.
This wizard may be in English only. However, the automatic fix also works for other language versions of Windows.
If you are not on the computer that has the problem, save the Fix it solution to a flash drive or a CD, and then run it on the computer that has the problem.
Let me fix it myself To manually retrieve the files, follow these steps:
Open the desktop, tap the folder icon, and then click Computer. Or, press the Windows logo key+E.
Double-tap or double-click the drive that Windows is installed on (typically, drive C).
Double-tap or double-click the Windows.old folder.
Double-tap or double-click the Users folder.
Double-tap or double-click your user name.
Open the folders that contain the files that you want to retrieve. For example, to retrieve files in the Documents folder, double-tap or double-click Documents.
Copy the files that you want from each folder and paste them to a folder in Windows 8. For example, if you want to retrieve everything from the Documents folder, copy all the files and folders from the Documents folder in the Windows.old folder, and then paste them to the Documents library in Windows 8.
Repeat steps 5-7 for each user account on your computer.
For more information about how to recover data from an earlier version of Windows, see Recover lost or deleted files.
You may not have ownership of a file or folder If you recently upgraded your computer to Windows 7 from an earlier version of Windows, some of your account information may have changed. Therefore, you may no longer have ownership of some files and folders. You might be able to resolve this issue by restoring your ownership of the files and folders.
To take ownership of a file or a folder, follow these steps:
Right-click the folder that you want to take ownership of, and then click Properties.
Click the Security tab, click Advanced, and then click the Owner tab.
Click Edit. If you are prompted for an administrator password or confirmation, type the password or provide confirmation.
Click the name of the person that you want to give ownership to.
If you want that person to be the owner of files and subfolders in this folder, select the Replace owner on subcontainers and objects check box.
You may have to recover files from the Windows.old folder If you recently upgraded your computer to Windows 7 from an earlier version of Windows, and you did not reformat your hard disk, you might still be able to access your old files from the Windows.old folder.
To fix this problem automatically, click the Fix it button or link. In the File Download dialog box, click Run, and then follow the steps in the Fix it Wizard.If you prefer to fix this problem yourself, go to the «Let me fix it myself» section.
This wizard may be in English only. However, the automatic fix also works for other language versions of Windows.
If you are not on the computer that has the problem, save the Fix it solution to a flash drive or a CD, and then run it on the computer that has the problem.
Let me fix it myself To manually retrieve the files, follow these steps:
Click Start, then click Computer.
Double-click the drive that Windows is installed on (typically, drive C).
Double-click the Windows.old folder.
Double-click the Users folder.
Double-click your user name.
Open the folders that contain the files that you want to retrieve. For example, to retrieve files in the Documents folder, double-click Documents.
Copy the files that you want from each folder and paste them to a folder in Windows 7. For example, if you want to retrieve everything from the Documents folder, copy all the files and folders from the Documents folder in the Windows.old folder, and then paste them to the Documents library in Windows 7.
Repeat steps 5-7 for each user account on your computer.
For more information about how to recover data from an earlier version of Windows, see Recover lost or deleted files.
